Introduction
Doc here. As you know, in many of our public analysis videos on YouTube, as well as in our members-only content and Telegram discussions, Oz frequently talks about Fair Value Gaps (FVGs). Since this concept plays a crucial role in technical analysis, I thought it would be a good idea to break it down for those who still find it unclear when analysing Bitcoin, Ethereum, and the wider crypto market.
What is a Fair Value Gap (FVG)?
A Fair Value Gap (FVG) is an imbalance in the market created when price moves aggressively in one direction, leaving an inefficiency in liquidity. This is visible on a chart when there’s a large, single-directional price movement with minimal to no trading occurring in between. These gaps often act as magnets for price, as the market seeks to “fill” these inefficiencies over time.
FVGs typically form in volatile market conditions when institutions or large players execute significant orders. Understanding how price interacts with these gaps can provide a strategic advantage in identifying future price movements.
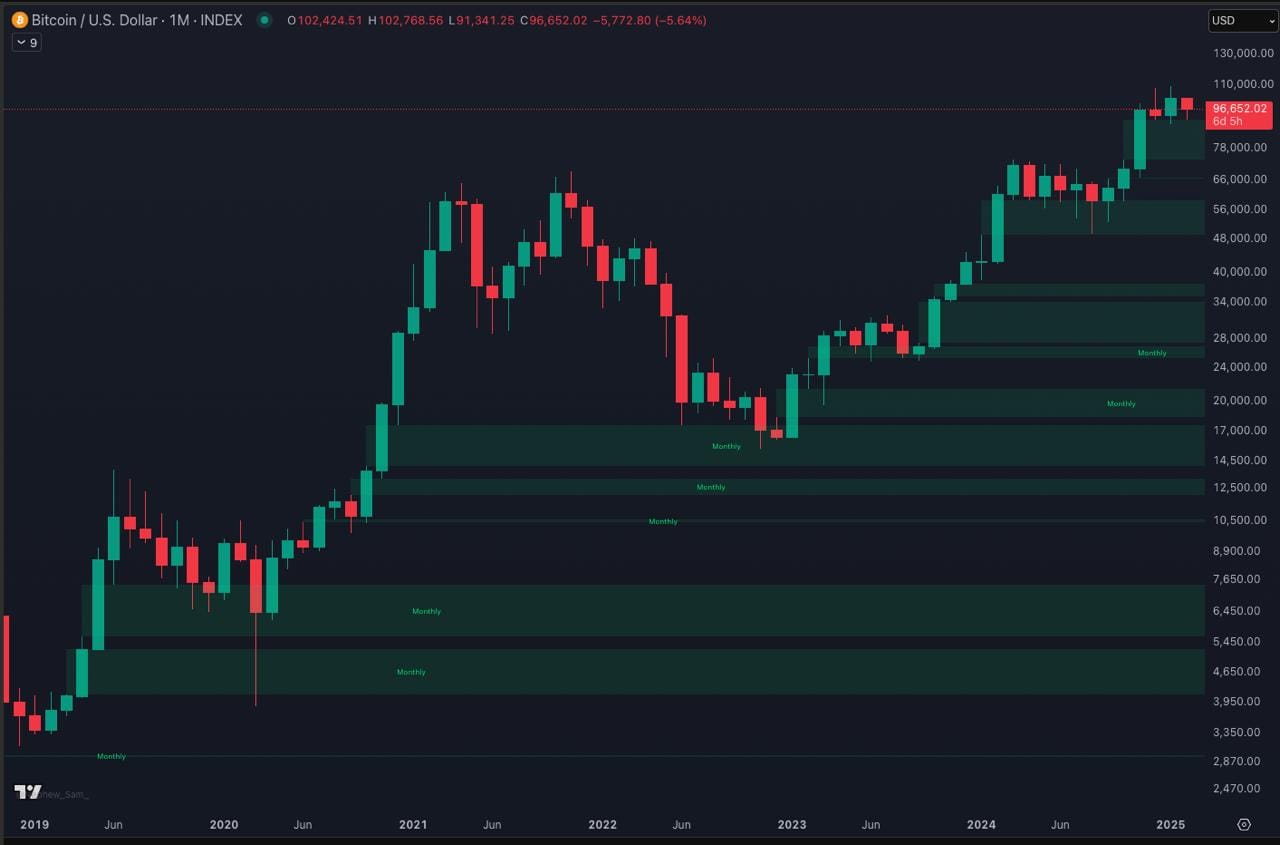
How Fair Value Gaps Form
Fair Value Gaps emerge during high-momentum moves when liquidity is taken out rapidly, leaving unfilled orders behind. This can happen due to:
- Strong Buy or Sell Pressure – Sudden surges in demand or supply cause aggressive moves.
- News-Driven Events – Economic reports, regulatory updates, or institutional buying can trigger imbalances.
- Thin Order Books – Low liquidity conditions often lead to large gaps in price action.
When an imbalance occurs, price tends to revisit these gaps to fill orders that were skipped during the initial move. This is where traders can anticipate key reactions.
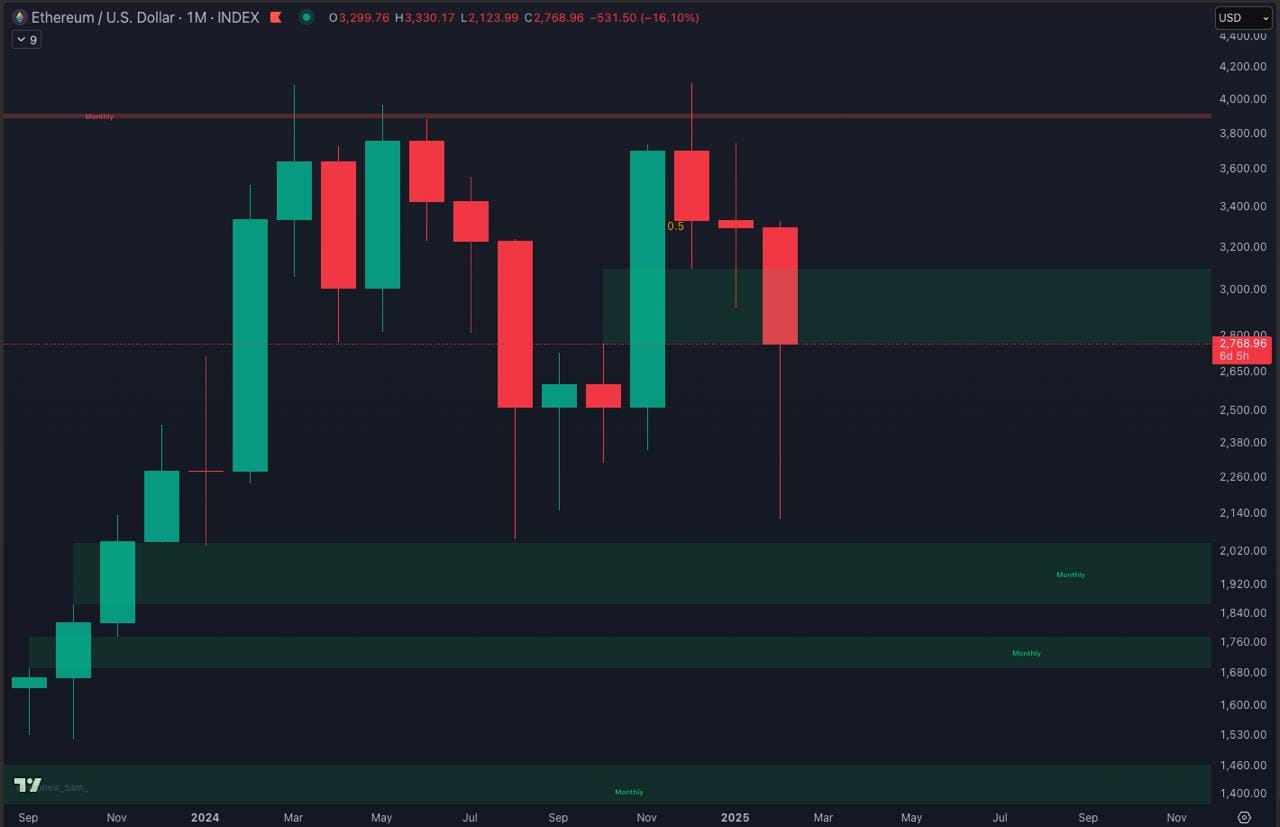
Identifying Fair Value Gaps on a Chart
Recognising FVGs is straightforward once you understand what to look for:
- Spot a Large, Single-Directional Move – Look for long-bodied candles with minimal wicks, indicating aggressive buying or selling.
- Check for Minimal Trading in the Middle – If price skips over a level without sufficient back-and-forth action, it likely contains an FVG.
- Use the Three-Candle Rule – A valid FVG typically appears between the high of one candle and the low of the third candle in a rapid move.
Once identified, these gaps can be used as areas where price may retrace before resuming the primary trend.
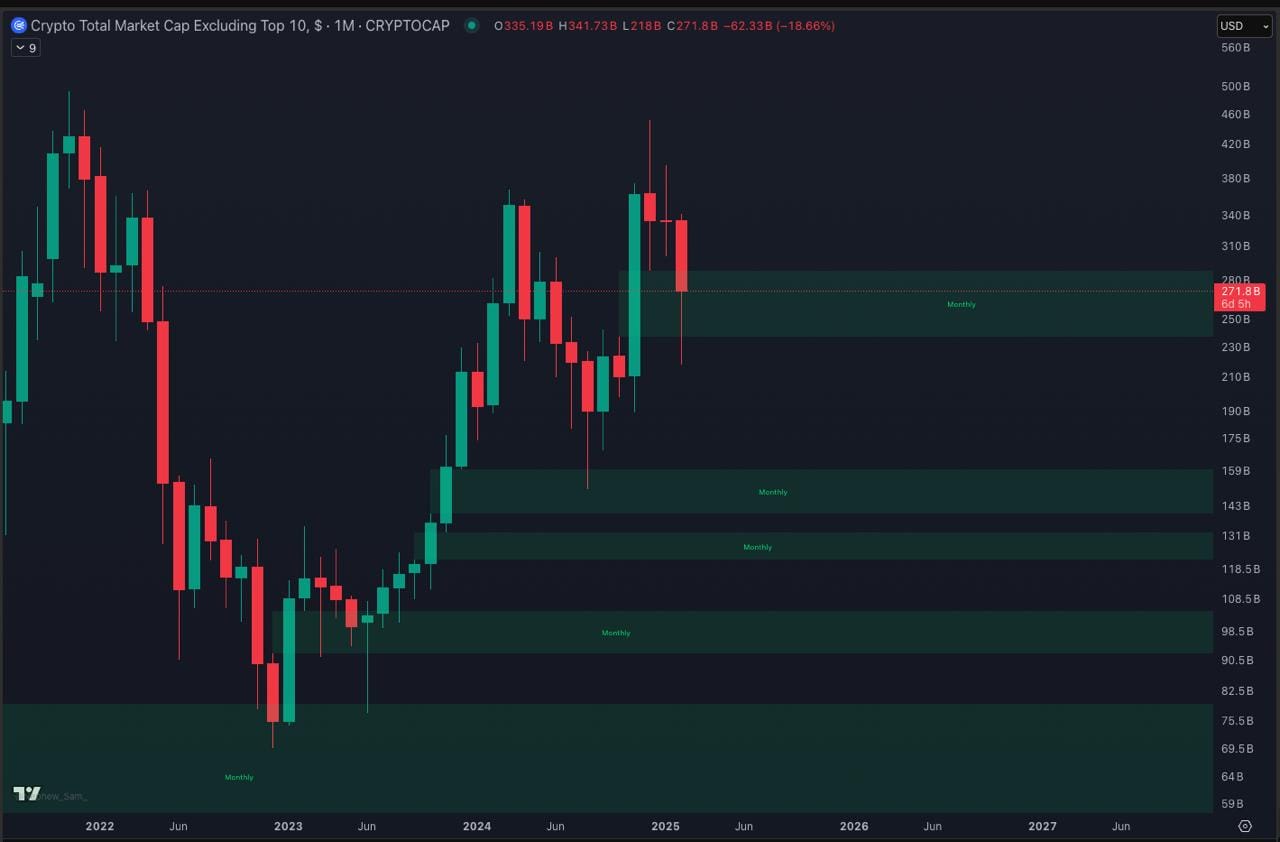
Why Fair Value Gaps Matter in Crypto Trading
FVGs serve as a technical roadmap for traders, providing potential entry points, exits, and risk management zones. Here’s why they are significant:
- Act as Liquidity Zones – Institutions often revisit FVGs to fill unexecuted orders.
- Predict Price Corrections – If price has moved too far too fast, it’s likely to pull back to an FVG before continuing.
- Enhance Confluence with Other Indicators – Pairing FVGs with support/resistance, Fibonacci levels, or moving averages can strengthen trade setups.
Understanding these gaps allows traders to avoid chasing price and instead anticipate where price is likely to return before its next major move.
How to Trade Fair Value Gaps
Traders use FVGs in several ways to refine their entries and exits:
1. FVG as a Reversal Zone
If price enters an unfilled FVG and stalls, it could indicate a reversal is forming. Confirmation from order flow and volume indicators can strengthen this setup.
2. FVG as a Continuation Entry
In trending markets, price often pulls back to FVGs before continuing in its original direction. Buying or selling at these retests can provide high-probability trades.
3. FVG in Confluence with Key Levels
Aligning an FVG with:
Increases the likelihood of the gap acting as a strong reaction area.
Common Mistakes When Trading FVGs
While Fair Value Gaps are a powerful tool, traders often make mistakes in their application:
✔ Blindly Entering Trades – Not every FVG will result in a price reaction. Wait for confirmation.
✔ Ignoring Trend Context – FVGs work best when aligned with the overall market structure.
✔ Overcomplicating Entries – Simplicity wins. Use FVGs alongside only a few key indicators, not everything at once.
✔ Failing to Manage Risk – Always set a stop loss. Just because price reaches an FVG doesn’t mean it has to reverse.

Final Thoughts
Fair Value Gaps are a crucial part of the technical analysis we use in our videos and discussions. They highlight areas of liquidity imbalance and give traders a strategic edge in anticipating price movements. However, FVGs should never be used in isolation—always combine them with confluence factors like volume, trend structure, and key support/resistance levels.
The market is full of liquidity traps and engineered moves designed to shake traders out. Recognising FVGs can help you avoid FOMO, enter trades at better locations, and improve your overall trading precision. Use them wisely, stay patient, and always trade with a plan.
Let me know if you have any questions, and I’ll cover more in the future.












Discussion